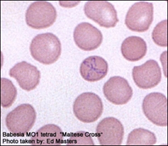
 Babesiosis is a Malaria-like illness caused by a parasite, either Babesia microti, B. duncani, B. divergens, MO-1.
Babesiosis is a Malaria-like illness caused by a parasite, either Babesia microti, B. duncani, B. divergens, MO-1.
It is sometimes fatal in the elderly or those with no spleen. Babesiosis may be more severe in patients with co-existing Lyme disease.
Symptoms include: fever, chills, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, sweats and anemia.
Tests for Babesiosis: blood smears, IFA (IgG & IgM), FISH (Flourescent in-situ Hybridization) and PCR may be ordered.*
* These tests were developed & performance characteristics determined by independent labs. They have not been cleared or approved by the FDA; however, the FDA has determined such clearance is not necessary. They are designd for clinical purposes and should not be regarded as investigational or for research.
Treatment is often atovaquone with azithromycin or clindamycin and oral quinine. Treatments vary, examples provided as information only.
Ticks that transmit babesiosis include Ixodes Scapularis (also called blacklegged tick or deer tick) and Ixodes Pacificus (western blacklegged tick) both of which also transmit Lyme disease. Multiple infections may be transmitted from the bite of the same tick.
Babesiosis has also been transmitted to humans through blood transfusions. In 2018, the FDA approved a test to screen the blood supply for Babesia microti.






