
SHARE THIS ARTICLE:
Study of Phenolic Compound, Gallic Acid, Against Borrelia Burgdorferi Shows Promise
Dr. Anna Goc, et al., published, “Inhibition of Borrelia Burgdorferi-Induced TLR2-NFκB Canonical Signaling by Gallic Acid through Targeting the CD14+ Adaptor Protein and p65 Molecule” in International Journal of Molecular Sciences on September 20, 2022. With the goal of discovering novel agents that work against B. burgdorferi, the researchers assessed the anti-Borrelia and anti-inflammatory effects of the phenolic compound, gallic acid.
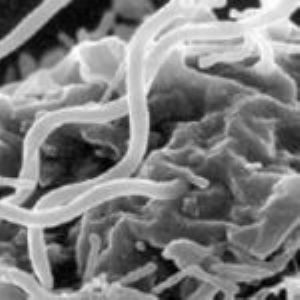
Results of the study demonstrated the biocidal effect of gallic acid starting from 100 μg/mL against active spirochetes, persisters/round-shaped bodies, and biofilm-like groupings of B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. Macrophages activation by live B. burgdorferi also caused robust NFκB-dependent proinflammatory responses that also occur with increases in the production of cytokines.
The study results show the effectiveness of gallic acid against B. burgdorferi and offer a potential mechanistic understanding of its TLR2/CD14+-NFκB facilitated mode of action. Additional studies on gallic acid and its potential to be used against Borrelia-caused infections are needed.
For More Information
Read the full study in International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
Read more peer-reviewed Borrelia Burgdorferi research.





